Page 4 - Anatomy & Physiology
P. 4
ch02.1.qxp 4/21/08 11:07 AM Page 33
The Human Body: Reading the Map 33
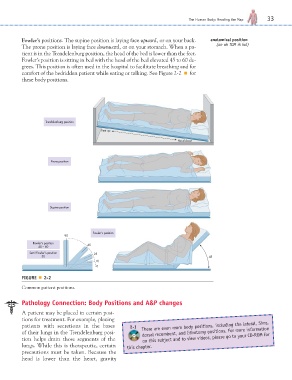
Fowler’s positions. The supine position is laying face upward, or on your back. anatomical position
The prone position is laying face downward, or on your stomach. When a pa- (an ah TOM ih kal)
tient is in the Trendelenburg position, the head of the bed is lower than the feet.
Fowler’s position is sitting in bed with the head of the bed elevated 45 to 60 de-
grees. This position is often used in the hospital to facilitate breathing and for
comfort of the bedridden patient while eating or talking. See Figure 2-2 ■ for
these body positions.
Trendelenburg position
Feet up
Head down
Prone position
Supine position
Fowler's position
90
Fowler's position
45 – 60 45
Semi-Fowler's position 25
30 45
10
0
FIGURE ■ 2-2
Common patient positions.
Pathology Connection: Body Positions and A&P changes
A patient may be placed in certain posi-
tions for treatment. For example, placing
patients with secretions in the bases 2-1 There are even more body positions, including the lateral, Sims,
of their lungs in the Trendelenburg posi- dorsal recumbent, and lithotomy positions. For more information
tion helps drain those segments of the on this subject and to view videos, please go to your CD-ROM for
lungs. While this is therapeutic, certain this chapter.
precautions must be taken. Because the
head is lower than the heart, gravity